All brakes are self-adjusting. Disc brake pad wear is automatically compensated, while drum brakes have an adjustment mechanism that is activated when the brakes are applied. The adjustment mechanism operates until the drum brake pads are worn to a thickness of 2 mm.
The hydraulic braking system consists of two diagonal circuits. The master cylinder has a separate reservoir for each circuit. In case of failure of one of the circuits, braking is still possible and is carried out by two wheels (one front and one rear). A dual control valve redistributes hydraulic pressure to prevent the rear wheels from locking up before the front wheels during hard braking. The control lamp on the instrument panel warns of a low level of brake fluid in the system. The lamp is turned on by a switch installed in the master cylinder reservoir.
The parking brake has an independent mechanical drive to the rear wheels. The parking brake lever is installed between the front seats.
The brake booster, mounted on a thermal shield in the engine compartment, uses manifold vacuum and atmospheric pressure to operate.
After completing work on any part of the brake system, take a test drive (always on a clean, dry and level road), to check the operation of the brakes. Check the operation of the brakes at various speeds by depressing the pedal either hard or soft. The car must stop smoothly, it should not lead to the side. Avoid blocking the brakes - this reduces the effectiveness of braking.
Tire condition, vehicle load, and wheel balance also affect braking performance.
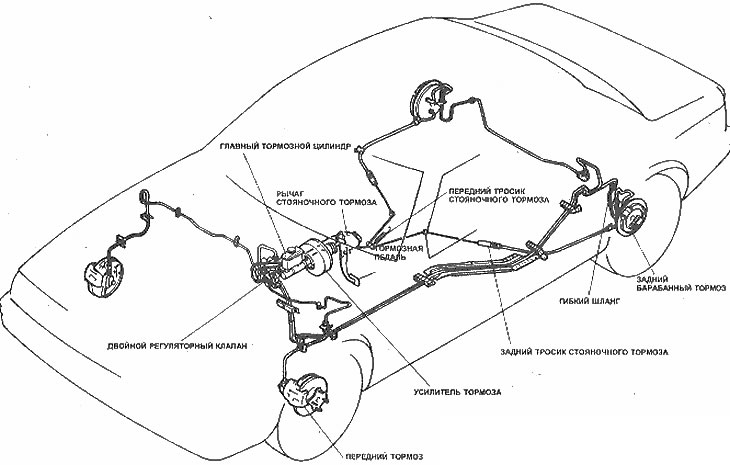
Arrangement of brake system components
