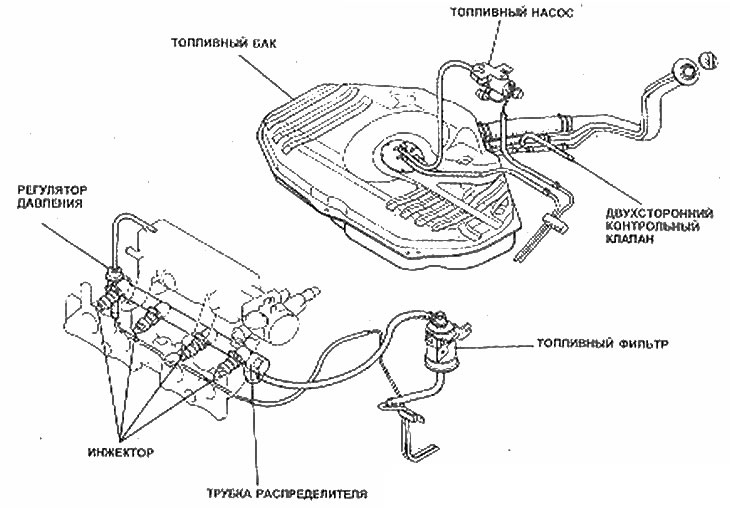
EGI System Inlet Parts
Details of fuel supply system EGI
Air flow meter
2. The air flow meter measures the amount of air that is drawn into the engine and, by means of a potentiometer, is converted into a voltage signal that is sent to the EGI control unit.
3. The meter also includes an intake air temperature sensor, an idle mixture bypass system, and a fuel pump control switch.
Throttle body
4. The throttle body is located upstream of the airflow meter and attached to the inlet expansion tank. It includes a throttle valve that is connected directly to the throttle control pedal.
5. It also includes an idle air bypass system, a throttle position sensor and a shock absorber to control throttle closing. The throttle position sensor sends signals to the EGI control unit.
Pneumatic valve
6. The pneumatic valve is located in the bypass hose around the throttle body. It consists of an electrically heated coil and a bimetallic plate. When the engine is cold, the valve is open and provides additional air to the additional cold start fuel for fast idling. During warm-up, the bimetal gradually closes the valve, thus returning the engine to normal idle speed.
Fuel pump
7. The fuel pump is located below the rear of the vehicle, next to the fuel tank. It is a concentric rotor including five rollers that move eccentrically within the spacer plate.
8. A diaphragm-type muffler at the outlet end of the fuel pump absorbs pressure pulses from the pump rollers, and a check valve is provided to remove residual pressure within the fuel lines when the engine is continuously running.
9. The purpose of the fuel pump wiring includes a control switch in the airflow meter that always turns the pump off when the engine is stopped.
Fuel injectors
10. Fuel injectors inject fuel into inlet ports. The amount of injected fuel, having determined the gay by the period during which the needle valve of the injector is open and this period, in turn, depends on the signal received from the EG1 control unit.
11. All four injectors fire simultaneously once per revolution of the crankshaft, ending with two injections for each 4-stroke cycle.
Fuel pressure control
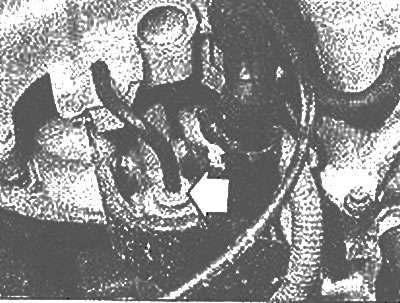
12. If the fuel pressure to the injectors were always constant, intake manifold vacuum changes would deliver the wrong amount of fuel even when the injection cycle is correct. Because of this, the pressure regulator (photo) adjusted to keep the fuel pressure 2.7 kg/cm2 higher than the intake manifold pressure.

Fuel pressure regulator - marked with an arrow (EGI engine)
Expansion tank
13. An expansion tank is included in the intake manifold to use acoustic wave impulses to push air into the cylinders during the intake stroke.
Fuel filter
14. The fuel filter is located in the engine compartment in the fuel supply line to the injectors. It separates any small particles that are detrimental to the operation of the injector needle valves.
EGI control unit
15. EGI control box (photo) processes information from engine sensors to control the injectors and idle solenoid valve. It also includes a digital test code that recognizes faults in the sensor circuits.
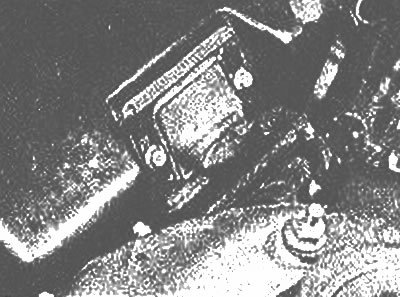
The EGI control unit is located below the dashboard
