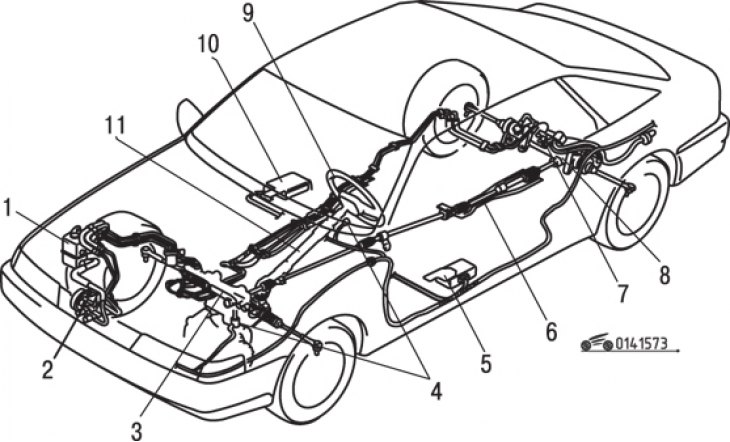
Pic. 15.72. All Wheel Steering System: 1 - reserve tank; 2 - oil pump; 3 – a steering mechanism of forward wheels; 4 – speed sensors; 5 - control unit; 6 – an intermediate shaft of a steering drive; 7 - traction relay; 8 - steering mechanism of the rear wheels; 9 - steering wheel; 10 - relay with timer; 11 - steering shaft
Some vehicles are equipped with an all-wheel steering system (4WS system) (pic. 15.72). This system connects the front wheel steering mechanism to the rear wheel steering mechanism, which is activated by a traction relay through the steering shaft, allowing the rear wheels to turn under certain conditions. Any maintenance work on the system (check and adjustment) should be carried out at a car service center.
Rear wheel bearing replacement
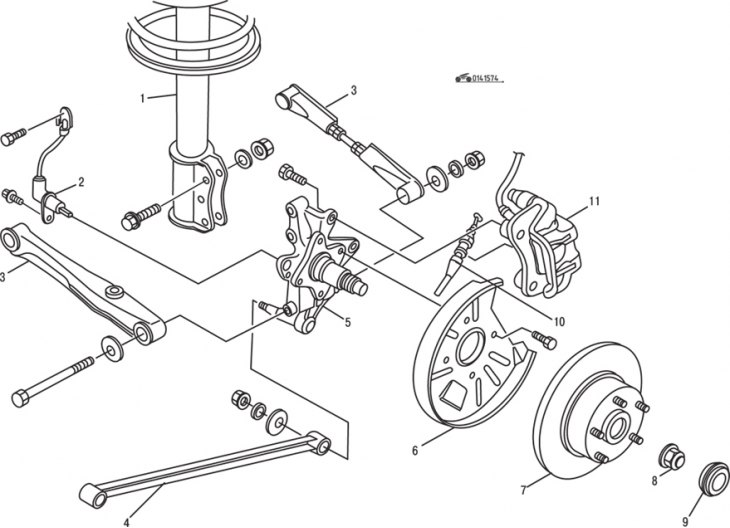
Pic. 15.74. Rear wheel suspension for 1988–1991 vehicles: 1 - shock absorber; 2 - wheel speed sensor of the ABS system; 3 - transverse lever; 4 – trailing arm; 5 - trunnion; 6 – a protective casing of a back brake; 7 - brake disc; 8 - nut (replace); 9 - hub cap (replace); 10 – parking brake cable; 11 - support
In cars since 1988, non-separable rear wheel bearings are installed that do not require adjustment (pic. 15.74). To replace, raise the vehicle and secure it on stands.
On vehicles equipped with rear disc brakes, remove the rear caliper with brake cylinder.
Remove the hub cap and unscrew the nut.
Remove the brake drum or disc.
If the bearing is damaged, press it out and press in a new one, for which it is necessary to hand over the hub to a car repair shop.
Install the hub on the axle, screw on a new nut and tighten it to the required torque.
Attention! On vehicles equipped with ABS, be careful not to damage the wheel speed sensors.
