Attention! On some models, when adjusting the ignition timing, it is mandatory to perform the work indicated on the information plate for reducing the toxicity of exhaust gases. The plate contains information on the preliminary operations that must be performed before adjusting the ignition timing, as well as the necessary technical data.
Checking and adjusting the ignition timing
Follow the preliminary ignition timing instructions on the VECI plate located under the hood.
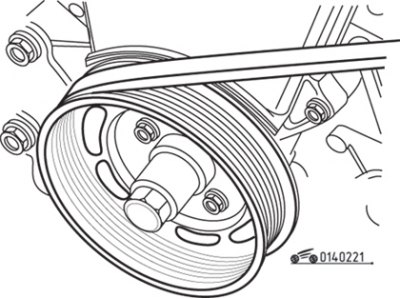
Pic. 2.21. Location of marks for setting the ignition timing
Near the crankshaft pulley there is a plate with a pointer, which is designed to align the pulley alignment mark with it. Label «T» corresponds to top dead center (TDC). The indicator plate is provided with a scale in 2°increments and an alignment mark corresponding to your vehicle model. If there is no setting mark, count away from the mark «T» desired number of degrees BDC as indicated on the VECI plate and mark this position on the plate. On some car models, instead of a plate, there is an ignition timing indicator and two notches on the pulley instead of one (pic. 2.21). Do not use the notch to set the ignition timing «vertex» (TDC).
In order for the mark on the pulley to be clearly visible when adjusting the ignition timing, mark it with chalk or paint.
Start the engine, warm it up to normal operating temperature and stop. Turn off all electrical consumers and disconnect the electrical connector from the radiator fan.
Ignition OFF, following the manufacturer's instructions, connect the stroboscope connector to the high voltage spark plug wire of number one cylinder.
Start the engine, point the strobe light at the mark on the crankshaft pulley and determine which alignment mark the notch on the pulley is aligned with.
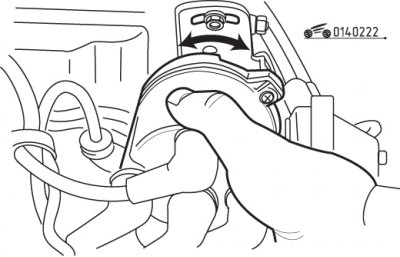
Pic. 2.22. Direction of rotation of the distributor when adjusting the ignition timing
If the notch is not aligned with the required mark, loosen the ignition distributor mounting bolt and turn it until the notch is aligned with the required alignment mark (pic. 2.22).
Tighten the ignition distributor mounting bolt and recheck the ignition timing.
Stop the engine and disconnect the stroboscope. Connect the spark plug wire of the first cylinder and the remaining elements that were disconnected.
Inspection and replacement of spark plugs
Use a jet of compressed air to clean the spark plug, which will prevent dirt from entering the engine cylinder after the spark plug is removed.
Attention! Manufacturers do not regulate the interval for replacing spark plugs, only indicate the need for regular inspection. In practice, the replacement of spark plugs must be carried out during maintenance, even if the spark plugs are in good condition.
Remove the spark plug.
If the spark plugs need to be replaced, only the spark plugs recommended for the engine should be used.
By the appearance of the turned out spark plugs, you can approximately assess the condition of the engine. A clean, white, non-tarnished spark plug insulator indicates a too lean air-fuel mixture. This appearance of the candle also indicates that the candle is too hot (heat is removed from the central electrode slowly). It is necessary to adjust the composition of the air-fuel mixture or replace the spark plug.
The deposition of dry soot is due to a mixture that is too rich. If the coating is black, oily, the engine is worn, it must be checked and repaired. If the insulator is covered with a light brown coating, then the mixture is optimal and the engine is in good condition.
Too large or too small an electrode gap, which changes the size of the spark, leads to a decrease in engine efficiency. The gap must always comply with the technical requirements.
It is checked with a wire gauge or feeler gauge. You can correct the gap by bending the side electrode with a special tool. In no case should the central electrode be bent - this can lead to breakage of the insulator and failure of the candle.
Before installing the spark plug in the engine, check that the threads are clean and undamaged. Clean it if necessary. Apply a special non-stick compound to the thread of the candle.
Inspect spark plugs for damage. If there are cracks in the insulator, the spark plug must not be used.
To screw in the spark plug several turns, use a piece of rubber hose into which, on one side, insert the spark plug insulator. The hose acts as a universal joint to align the spark plug with the threaded hole. If the spark plug is screwed in at an angle, the hose will rotate on the spark plug insulator without damaging the threads. Screw in the spark plug a few threads, remove the hose, then screw in and tighten the spark plug with a wrench.
Use a torque wrench to tighten the spark plug. If a torque wrench is not available, tighten the spark plug no more than 1/4 turn from the point where the spark plug washer contacts the sealing surface.
Before connecting the high voltage wire to the spark plug, check its condition.
Turn the end of the high voltage wire to the new spark plug, it should be securely fixed on the spark plug. Make sure the wire runs some distance from the exhaust manifold.
Replace the remaining spark plugs in the same way, replacing them one at a time so as not to mix up the high voltage wires.
Check and replacement of high-voltage wires of spark plugs, cover and rotor of the ignition distributor
High voltage wires must be checked each time spark plugs are installed. Start a visual check with the engine running. In a darkened garage, start the engine and watch every wire. If an internal wire break is detected, an electrical arc or spark will be visible at the fault. If there is an electric arc, replace the wire.
Start up and cool the engine then check a cover and a rotor of the distributor of ignition.
Disconnect the wire from the negative battery terminal.
To avoid confusion, remove and inspect the high-voltage wires one at a time.
Pulling up and turning at the same time, remove the tip with the high voltage wire from the spark plug.
Do not remove the handpiece by pulling directly on the high voltage wire.
Check the inside of the tip for signs of corrosion, which is a white solid powder.
Reinstall the tip with the high-voltage wire by pressing it and turning it at the same time until it locks into place.
Wipe the high-voltage wire along its entire length with a clean rag, removing dirt and grease from it. Check the wire for burns, cracks, or other damage. Do not bend the wires too much, as the inner conductor may break. Use an ohmmeter to measure the resistance of the center conductor in each wire. Nominal resistance 16 kOhm/m.
Check the inside of the protective cover for signs of corrosion. Reconnect the high voltage wire.
Similarly, check the condition of the remaining high-voltage wires.
Turn out screws and remove a cover of the distributor of ignition. From the inside, check the cover for cracks, carbon tracks, burns and unreliable contacts.
Turn out two screws and remove a rotor of the distributor of ignition. Check the rotor for cracks, carbon tracks, burnt side and center electrodes.
In the presence of any damages replace a cover and a rotor of the distributor of ignition. It is recommended that when replacing high-voltage wires, also replace the cover and rotor of the ignition distributor.
Check the centrifugal ignition timing for damage, corrosion and damaged springs. While holding the distributor shaft, rotate the centrifugal governor housing and check that the governor weights move smoothly and the spring tension is in the opposite direction.
Establish a cover of the distributor of ignition, then connect a wire to the negative plug of the storage battery.
Attention! It is important to replace the wires one at a time and mark their connection points, as each wire ensures the correct firing order of the cylinders.
