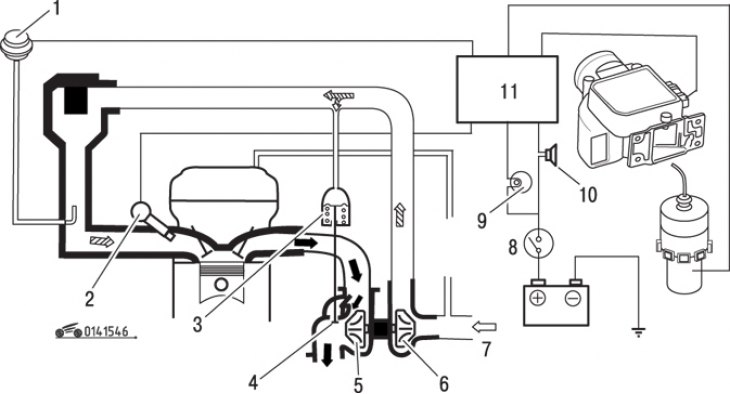
Pic. 15.46. Turbo Charging: 1 - pressure sensor; 2 - nozzle; 3 – actuator; 4 - bypass valve; 5 – turbine wheel; 6 - turbocharger; 7 - from the air flow meter; 8 - ignition switch; 9 – a control lamp of a turbocompressor; 10 - warning buzzer; 11 - control unit
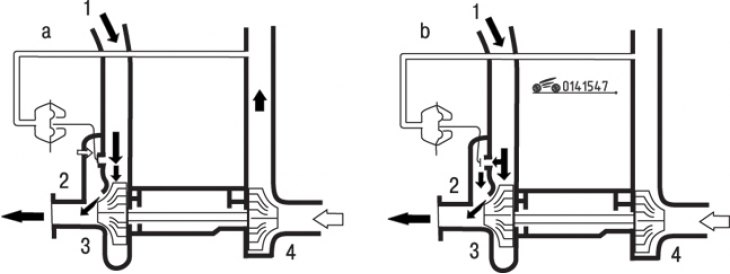
Pic. 15.47. Scheme of operation of the turbocharger bypass valve: a - the valve is closed; b - the valve is open; 1 - flow of exhaust gases; 2 - bypass valve; 3 – turbine wheel; 4 - turbocharger wheel
The turbocharging system is designed to boost the engine by increasing the pressure of the air-fuel mixture at the inlet to the combustion chamber using a turbocharger driven by the exhaust gas flow (pic. 15.46). Turbocharging improves the filling of the cylinders with the air-fuel mixture. Air pressure in the intake manifold is controlled by a turbocharger wastegate integrated with an actuator (the valve is actuated by a spring-loaded rod, which moves under the action of pressure on the intake manifold). The valve directs part of the exhaust gases past the turbine blades, thereby regulating the amount of forced air (pic. 15.47). On later turbocharged models, an intercooler is installed to cool the air at the inlet of the turbocharger (fig.15.47).
Turbocharger check
The design of a turbocharger is relatively simple, but this precision unit can easily fail if the oil or coolant supply is interrupted, or due to loosening or mechanical damage to the pipelines. Diagnosis and maintenance of the unit is carried out according to certain methods using special equipment, therefore, to troubleshoot, you should contact a car service center or a specialized workshop. However, in garage conditions, you can check the integrity and correctness of the connections, as well as the tightness of the system, remove and install the turbocharger, thereby saving on the cost of replacing it.
Each turbocharger has its own noise during operation, so a change in the noise characteristic of this unit may be a sign of a malfunction. A high-pitched whistling sound may indicate a gas leak from the intake or exhaust manifold. If the turbocharger makes an unusual sound, take it to a car service or specialist workshop for repair. Periodically inspect the exhaust manifold as no cracks or loose connections are allowed. Turbine speeds are up to 140,000 min-1, so a loss of coolant or contamination of the bearing oil can cause serious damage. Check the tightness of the pipelines supplying coolant and oil. A sign of leakage is traces of burnt oil on the casing of the turbocharger.
Attention! The replacement of engine bearings, such as main bearings, connecting rod bearings or camshaft bearings, should be combined with flushing the turbocharger with clean engine oil.
Removal and installation of a turbocharger
Drain coolant from a cold engine.
Remove the ignition distributor.
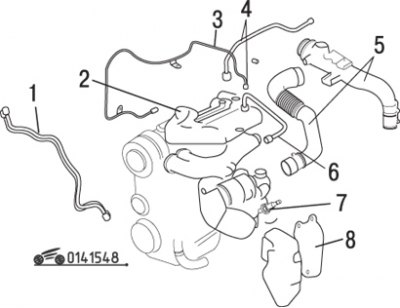
Pic. 15.48. Elements of the turbocharging system: 1 - air tube; 2 - upper insulating casing; 3 - oil pipeline (to the turbocharger); 4 - secondary air tube; 5 - air intake and air hose; 6 - recirculation valve tube; 7 – oxygen concentration sensor; 8 - lower insulating casing
Remove the air intake and air hose (pic. 15.48).
Remove the air tube.
Remove the bottom insulating casing.
Remove the secondary air supply tube.
Remove the oil line from the turbocharger.
Remove the top insulating casing.
Disconnect the recirculation valve tube from the exhaust manifold.
Remove coolant hoses.
Remove the oxygen concentration sensor from the exhaust manifold.
Remove the front exhaust pipe from the catalytic converter.
Loosen the bolts securing the turbocharger to the bracket.
Remove the exhaust manifold mounting bolts and remove the turbocharger assembly with the exhaust manifold and front pipe.
Remove the nuts securing the exhaust manifold and front pipe to the turbocharger.
Check the radial and axial play of the turbocharger rotor. If axial or radial play is felt, the turbocharger must be replaced.
Before installing, lubricate the turbocharger bearings by injecting 25 cm3 of engine oil into the turbocharger lubrication hole.
Attach the exhaust manifold and front pipe to the turbocharger. Replace gaskets. Tighten the nuts to the required torque.
Further installation is carried out in the reverse order of removal.
Before starting the engine, disconnect the wire from the negative terminal of the ignition coil. To increase the oil pressure and fill the lubrication system, turn the engine crankshaft for 20 with the starter. Connect the wire to the negative terminal of the ignition coil and start the engine. It is possible to increase the engine crankshaft speed no earlier than 30 s after starting.
