Hot air system
Operations for checking the hot air supply system are described in subsection 5.1.1.
Intake manifold heater
Intake manifold heater system diagram
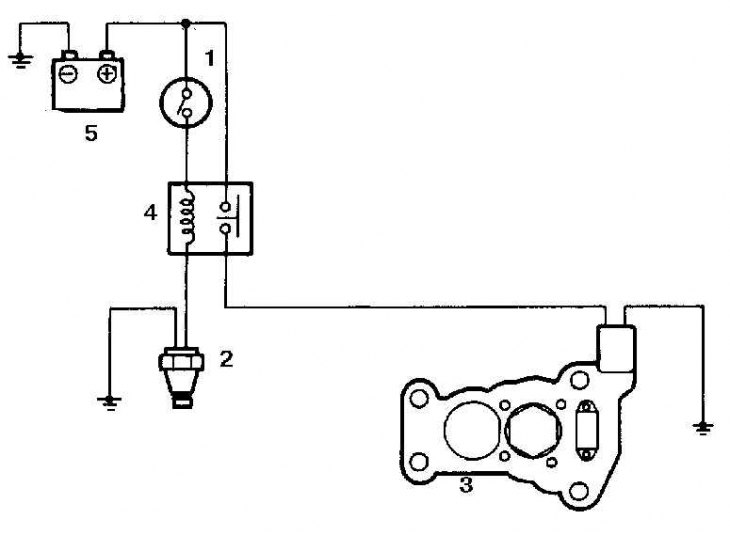
1. Ignition switch
2. Temperature switch heated by engine coolant
3. Intake manifold heater
4. Heater relay
5. Battery
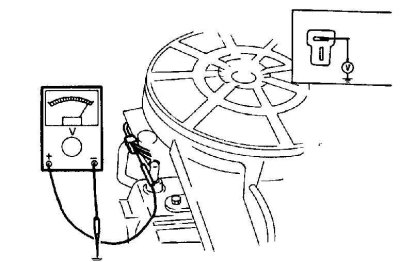
1. When the engine is cold (coolant temperature below 60°C), connect a voltmeter between the power wire on the heater (usually a thick red wire) And "weight". If the voltmeter does not register battery voltage, check the temperature switch and heater relay.
2. Connect a voltmeter between the heater ground wire (black wire) And "weight" car. The voltage recorded by the voltmeter should be very low (0.25 volts or less). If the voltage is higher, check that the heater is properly grounded.
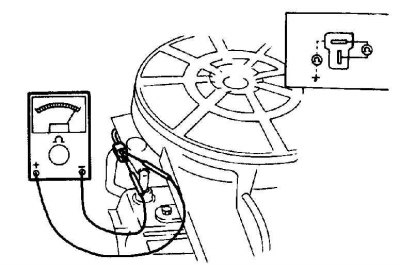
3. Disconnect the heater connection wires and connect an ohmmeter between them. Replace heater if there is no continuity (resistance should be 1.0 ohm or less).
Temperature switch
1. Connect a voltmeter between the power wire of the temperature switch and "weight". The recorded voltage must be very low (0.25 volts or less), since grounding is carried out through a temperature switch.
2. If the recorded voltage exceeds 0.25 volts, then the temperature switch is partially or fully open. Check this by disconnecting the wires and connecting an ohmmeter between the temperature switch terminals. The ohmmeter should indicate that the circuit is open if the switch is open and therefore the switch is faulty. If the ohmmeter shows that the circuit is closed (which indicates that the switch is working), check the ground wire connecting the switch to "weight" car.
3. Disconnect the ground wire, the power wire should be at the nominal voltage of the battery. If not, check the heater relay.
4. When the engine is hot (coolant temperature above 60°C) and the ignition is on, the voltage on the power wire of the temperature switch must be equal to the rated voltage of the battery, since the circuit must be opened by the switch.
5. If the recorded voltage is lower, test the temperature switch for continuity as described above. The switch should open the circuit when the engine is hot, if not, then it is faulty.
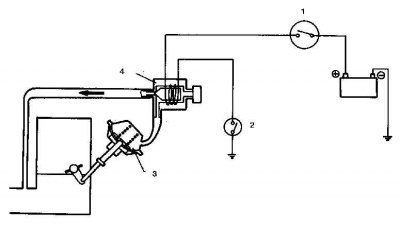
Heater relay
Intake manifold heater relay circuit
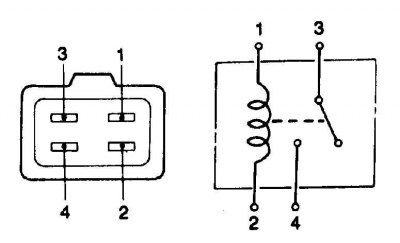
1. With the ignition on, check that terminal 1 has nominal battery voltage. If there is no potential, check the connecting wires up to the ignition switch.
2. Check for nominal battery voltage at terminal 3 (when the ignition is on or off). If there is no potential, check the connecting wires to the battery.
3. Temporarily ground terminal 2 and check for battery voltage at terminal 4. If there is no potential, replace the relay.
Fuel cut-off valve
1. Turn on the ignition and then turn it off; the valve should click when the key is turned in the ignition switch.
2. Connect a voltmeter between the valve power wire and "weight". If the voltmeter does not show battery voltage, check the connecting wires to the power source (power is turned on by the ignition switch).
3. Check the function of the valve plug by disconnecting the check valve connector. Temporarily connect the positive battery terminal and the valve power wire, and the negative battery terminal and the solenoid valve body with a loop wire (or valve ground wire, if available).
4. Apply and remove voltage several times and check the clarity of the stroke of the plunger. Replace the valve if it is defective and cleaning will not improve its performance.
Low RPM Fuel Cutoff System (if installed)
Terminal "masses" on the connection socket
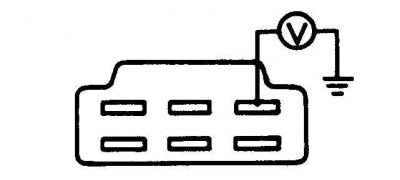
1. Connect a voltmeter between terminal "masses" on the valve connector and "weight" car.
2. When the engine is idling, the voltage should be less than 1.5 volts.
3. Increase the crankshaft speed; when the crankshaft speed rises above 2300 rpm, the voltmeter should show the rated voltage of the battery.
The system of lean fuel mixture with a decrease in the frequency of rotation of the crankshaft
Using a Voltmeter to Test the Lean System
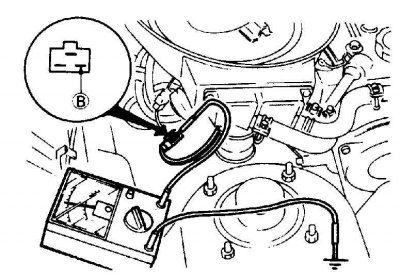
B. Lean fuel valve terminal
1. Warm up the engine to normal operating temperature, then connect a voltmeter between the "IN" at the lean fuel mixture valve connection connector and "weight".
2. Raise the engine speed to about 3000 rpm. The voltage recorded by the voltmeter should be close to zero.
3. Close the throttle quickly and as the engine speed decreases, the valve should make a hissing sound; The voltmeter reading should drop to zero. The voltmeter reading should then increase to the nominal battery voltage as the engine speed drops below about 2100±100 rpm.
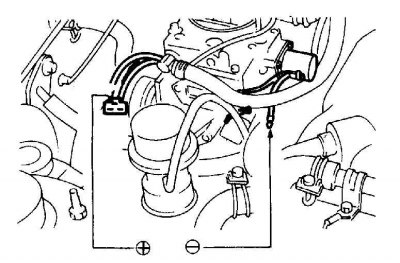
4. Check valve plunger travel by disconnecting the lean fuel system valve connector. Connect the positive terminal with a jumper wire (+) battery and valve power terminal and the second jumper wire negative terminal (-) battery and ground wire.
5. Apply and remove voltage several times; the valve should click when applying and releasing voltage.
Idle system switch
Using a voltmeter to test a switch
1. Adjusting screw
1. Connect a voltmeter between the two terminals on the idle switch connector; when the engine is idling, the voltage should be zero.
2. Raise the engine speed above 1250±50 rpm; The voltmeter should register the nominal voltage of the battery.
The system of enrichment of the fuel mixture with a decrease in the frequency of rotation of the crankshaft
Using a voltmeter to check the enrichment system
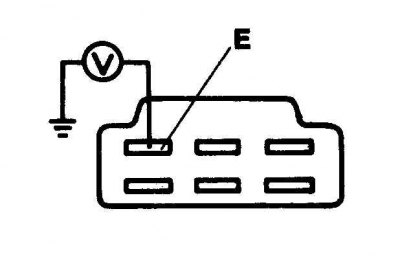
E. Klemma "masses" solenoid valve
Supplying power directly to the enrichment system solenoid valve
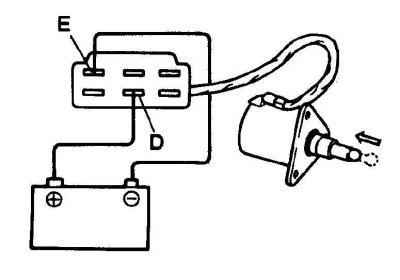
D. Solenoid valve power terminal
E. Klemma "masses" solenoid valve
1. Warm up the engine to normal operating temperature, then connect a voltmeter between the "E" on the connector for connecting the valve of the fuel mixture enrichment system and "weight".
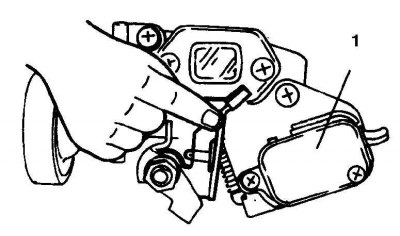
2. Raise the idle switch lever to open the circuit (1 – the switch of system of idling).
3. Open the throttle and raise the engine speed to about 3000 rpm. When the crankshaft speed increases above about 2300 rpm, the voltage recorded by the voltmeter should be equal to the rated voltage of the battery.
4. Close the throttle quickly and when the crankshaft speed decreases to 2300–1500 rpm, the voltmeter reading should drop below 1.5 volts. When the crankshaft speed drops below 1500 rpm, the voltmeter reading should increase to the nominal voltage of the battery.
5. Check valve plunger travel by disconnecting the enrichment system valve connector. Connect the positive terminal with a jumper wire (+) battery and valve power terminal and the second jumper wire negative terminal (-) battery and valve ground wire.
6. Apply and remove voltage several times; the valve should click when applying and releasing voltage.
Throttle damper (installed on some models)
Throttle damper adjustment
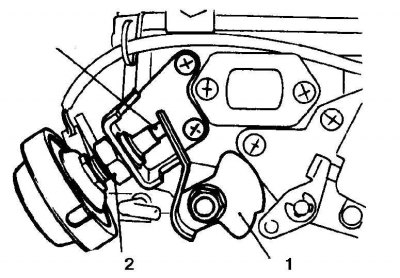
1. Lever
2. Locknut
3.Stem
1. Warm up the engine to normal operating temperature and check for proper idle speed and idle mixture adjustment
2. Leave the engine to idle, then open the throttle and raise the engine speed to 3000 rpm.
3. Fully close the throttle; the damper rod should touch the throttle lever at a crankshaft speed of 2200±100 rpm.
4. Adjust the throttle damper so that the damper rod touches the throttle lever at the specified engine speed.
5. Release the accelerator pedal and the damper should slowly return the throttle lever to the idle position.
Throttle Positioning Mechanism (installed on some models)
Checking the throttle positioning system
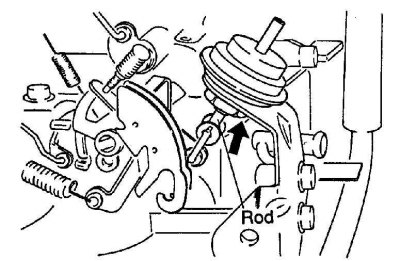
1.Stem
1. Let the engine idle, then slowly open the throttles and raise the engine speed to about 3000 rpm. When the crankshaft speed rises above about 2000 rpm, the diaphragm rod of the positioning system should be retracted by the diaphragm.
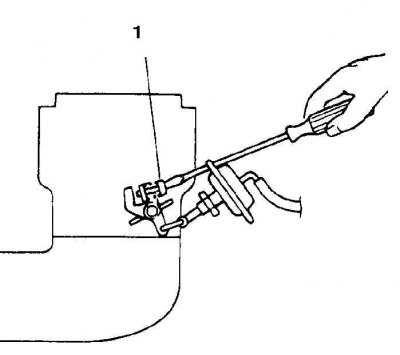
2. Close the throttle slowly; when the engine speed drops below about 1600-1800 rpm, the positioner rod must be released to close the throttle.
Throttle Positioning Diaphragm
Diaphragm check
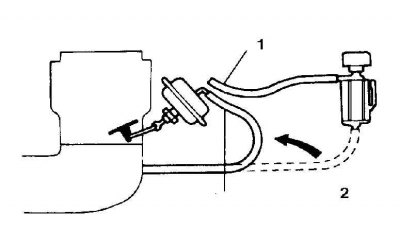
1. Disconnect the vacuum hoses from the diaphragm and plug the hose fitting to the solenoid valve (if installed).
2. Connect a vacuum pump to the vacuum port on the diaphragm and evacuate the air to obtain a vacuum of 300 mHg; the diaphragm must fully retract the stem and the vacuum must be maintained for at least 30 seconds. Replace the diaphragm if it is defective.
Adjustment
1. When the engine is idling (and all electrical equipment is turned off), disconnect the diaphragm vacuum hose connecting it to the throttle position solenoid valve.
2. Connect the vacuum hose from the intake manifold to the nozzle on the diaphragm, passing the solenoid valve of the throttle positioning system; the engine speed should rise to 1050–1250 rpm.
3. Connect the hose from the intake manifold vacuum connection to the connection on the diaphragm.
4. Connect a voltmeter between terminal "masses" on the solenoid valve connector and "weight" car.
5. Adjust the diaphragm linkage by turning the adjusting screw in the desired direction.
Throttle position solenoid valve
Checking the solenoid valve of the throttle positioning system
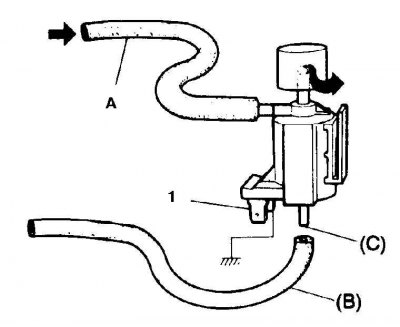
A. Hose from intake manifold
B. Hose to Throttle Position Diaphragm
C. Spigot
1. Supply voltage at 12 volts
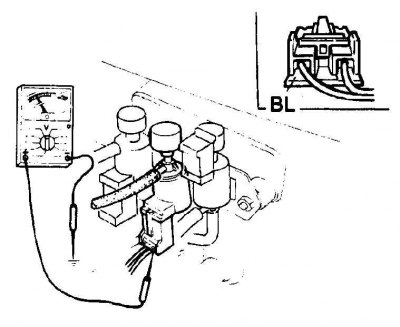
1. Connect a voltmeter between the ground terminal on the solenoid valve connector and "weight" car; when the engine is idling, the voltage indicated by the voltmeter should be almost zero.
2. Raise the engine speed to about 3000 rpm and the voltmeter should show a voltage approximately equal to the battery voltage.
3. Slowly close the throttle, reducing the engine speed to about 1600-1800 rpm; The voltmeter reading should drop to almost zero.
4. When the engine is idling, disconnect the vacuum hose connecting the solenoid valve and the vacuum diaphragm from the nozzle on the solenoid valve; there must be no vacuum in the pipe.
5. Disconnect the connection connector and connect the positive terminal of the battery and the wire to the power supply terminal of the solenoid valve with a jumper wire.
6. Connect the negative terminal of the battery and the ground terminal of the solenoid valve with a loop wire; a vacuum should form in the vacuum pipe.
7. If the valve does not function as expected, check the connecting wires of the solenoid valve and the electronic control unit and, if they are in order, check the electronic control unit.
8. Connect the vacuum hose and connection connector after completing the test.
System for increasing the speed of the crankshaft when idling (models with hydraulic power steering)
Scheme of the idle speed increase system when the power steering system is turned on
1. Ignition switch
2. Power steering switch
3. Aperture
4. Solenoid valve (controlled by a switch in the power steering system)
When the engine is idling, turn the steering wheel; the throttle positioning system should activate and increase the engine speed. If not, carry out the following checks.
Idle system temperature compensator at high engine temperature
Idle system temperature compensator at high engine temperature
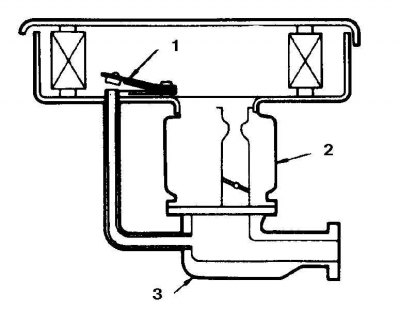
1. Compensator valve
2. Carburetor
3. Intake manifold
1. Remove the air filter.
2. Disconnect the vacuum hose going to the temperature compensator from the nozzle on the carburetor and connect a vacuum pump to this hose.
3. Measure the temperature near the temperature compensator; below 67°C the compensator must be closed. At temperatures above 71°C, the compensator must be open.
4. Wait until the temperature of the compensator drops below 67°C. Using a vacuum pump, pump out air to obtain a vacuum of 500 mmHg; this pressure must be maintained for at least 10 seconds. If not, then the temperature compensator valve is partially or fully open and needs to be replaced.
5. Heat the temperature compensator to a temperature above 71°C; use a vacuum pump to pump out air - the pressure should not drop. If a vacuum is formed, then the temperature compensator valve is not fully open and must be replaced.
Automatic choke
Power check
The operation for checking the power supply of the automatic air damper is described in subsection 5.1.1).
