Examination
1. Inspect the unit for cracks and signs of corrosion or rust. Inspect the threads of the block holes. If defects are found, the unit must be repaired or replaced if possible.
2. Examine the cylinders.
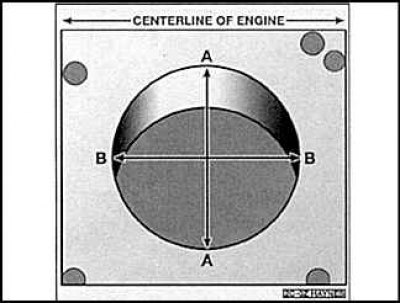
3. Measure the diameter of the cylinder perpendicular to the center line (A) and parallel to the center line (IN).
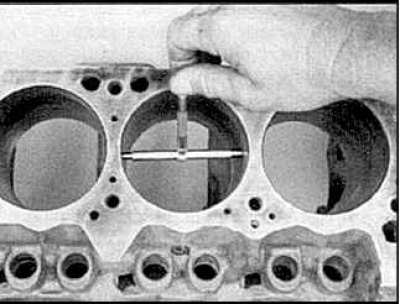
4. Measure the cylinder diameter with a gauge.
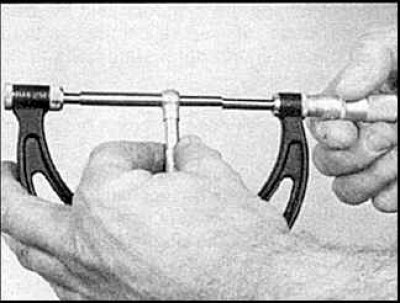
5. Measure the length of the gauge with a micrometer.
6. Measure the diameter of each cylinder at the top, middle and bottom, parallel to the axis of the crankshaft.
7. Measure the diameter of each cylinder in the upper middle and lower parts of it, perpendicular to the axis of the crankshaft.
8. The taper of a cylinder is calculated as the difference between the top and bottom diameters. Ovality is the difference between parallel and perpendicular measurements.
9. If the results obtained do not match the technical requirements, contact the experts.
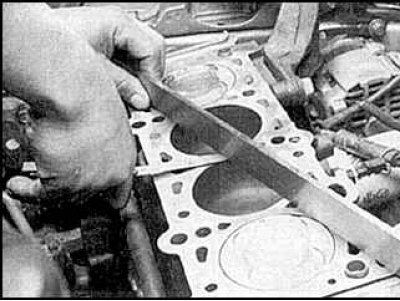
10. Using a ruler and feeler gauges, check that the surface of the block mating with the head is not deformed.
11. Check piston and cylinder wear with feeler gauges. If you find wear or damage when inspecting the unit, contact a specialist.
Cleaning
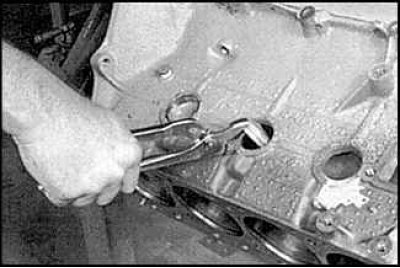
1. Remove the soft plugs from the cylinder block. To do this, use a hammer and a mandrel to sink them into the block, and then remove the plugs from the holes by picking them up with large pliers.
2. Remove any remaining gasket material from the cylinder block with a spatula, being careful not to damage the surface.
3. Remove the main bearing caps and remove the bearings from the block and caps. Inscribe which cylinder the bearing belongs to, as well as the part from which it was removed (from the cover or cylinder block), put them separately from each other.
4. With special hex socket wrenches (Allen key) Turn out and remove all carving plugs of channels of the block of cylinders.
5. If the engine is heavily soiled, it should be taken to a car service workshop for washing with a strong jet or in a hot chamber. Almost all car dealerships sell brushes for cleaning oil channels and holes. Rinse the internal passages with a stream of warm water until the water runs clear, dry the unit thoroughly, and coat the treated surfaces with oil to prevent corrosion. If compressed air is available, blow out the block and internal passages to speed up the drying process.

6. If the block is slightly dirty, it is enough to wash the block with warm water and detergent and a stiff brush. Take your time and do this job carefully. Regardless of the flushing method, clean the oil channels and holes very carefully, dry the block and lubricate the treated surfaces with oil.

7. The threaded holes in the block should be tapped to ensure correct torque readings during assembly. Passing with a tap will clean the threaded holes from dirt, corrosion and sealant residues, as well as restore the thread. If possible, blow out holes with compressed air to remove material residue from the tap.
8. Thoroughly clean the threads of the cylinder head bolts and main bearing caps.
9. Reinstall the main bearing caps, hand-tighten the bolts.

10. Install new plugs into the block, having previously lubricated them with high-temperature sealant. Make sure that the plugs fit correctly, that there are no distortions. otherwise, leaks may occur.
11. To fit the plugs, you will need a special tool, but this operation can be performed with the same quality using a mandrel, the diameter of which corresponds to the plug hole, and a hammer.
12. If the engine is not being assembled at the moment, then cover the cylinder block with a plastic cover, which will protect it from contamination.
