2. Inspect the crankshaft bearings for signs of wear, scratches, corrosion, or cracks.
3. Remove nicks around oil holes and clean holes with solvent.
4. Inspect the crankshaft for cracks or other damage.
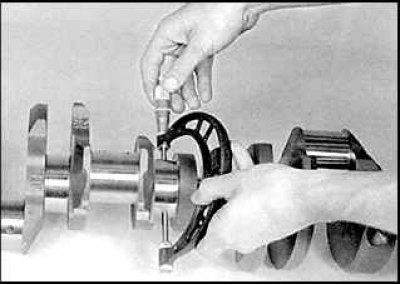
5. Measure the diameters of the main and connecting rod bearings. To identify taper and ovality, measure the diameter of each of the bearings at several points. If necessary, the crankshaft must be processed in a specialized workshop.
6. Check the crankshaft seal journals for signs of wear or damage. If the seals have worn out the grooves on the journals, then the new seals will leak oil.
7. Measure the thread length of each of the main bearing cap bolts. Bolt threads must be no longer than 67.5 mm on four-cylinder engines and no longer than 136 mm on six-cylinder engines (for long bolts) and 119 mm (for short bolts), otherwise the bolts must be replaced.
