2. Using a wire brush or fine sandpaper, clean the piston head from deposits.
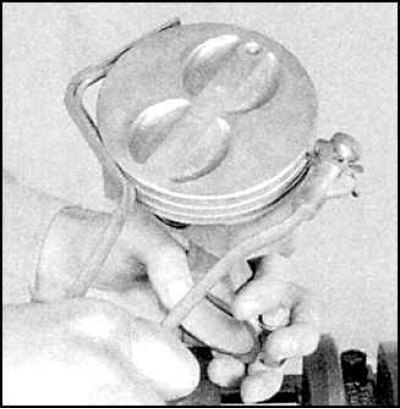 |  |
3. Clean the piston ring grooves with a special tool or a piece of a broken piston ring.
4. After removing all deposits, clean the pistons and connecting rods with a solvent and dry them.
5. If the pistons and cylinder walls are not badly worn and the cylinders have not been bored, new pistons do not need to be installed.
6. Carefully inspect all pistons for cracks on the piston skirt and on the surface around the connecting rod pin.
7. Inspect pistons for scratches, nicks, burnt areas, or corrosion.
8. If the piston skirt is severely scratched, the cause is overheating or abnormal combustion of the fuel mixture. In this case, it is necessary to carefully check the lubrication and cooling systems of the engine. The presence of a hole in the piston head indicates abnormal combustion of the fuel mixture (pre-ignition occurs). Causes may be a leak from the intake manifold, poor fuel mixture, incorrect ignition timing, exhaust system malfunctions.
9. Corrosion spots on the piston mean coolant is leaking into the combustion chamber.
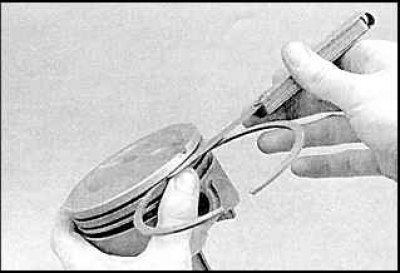
10. Measure the side clearances of the piston rings. If the clearance exceeds the allowable limits, the piston must be replaced.
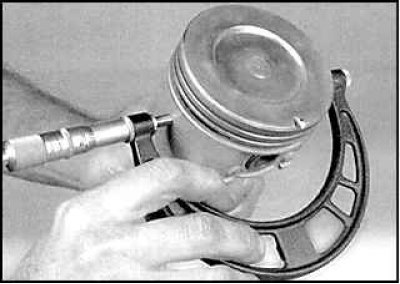
11. Measure the clearance between the piston and the cylinder, to do this, measure the diameter of the piston perpendicular to the piston pin and measure the diameter of the cylinder. Subtract the piston diameter from the cylinder diameter. If the gap exceeds the allowable limits, the cylinder must be bored and a new piston and new piston rings installed.
12. Check clearance between piston and connecting rod.
13. Inspect the connecting rods for cracks or other damage. For a more detailed verification of pistons and connecting rods, contact the experts.
14. Measure the thread length of the connecting rod bolts. In four-cylinder engines, the bolt threads must be no longer than 45 mm, and in six-cylinder engines no longer than 48 mm, otherwise the bolts must be replaced.
