Attention! Gasoline is a flammable liquid, so when working with any element of the fuel system, take all fire safety measures. See warnings at the beginning paragraph 2.
1. Before starting work, relieve pressure in the fuel system (see paragraph 2).
2. Fuel supply and return pipelines, as well as tank ventilation pipelines pass from the fuel tank to the engine compartment. The pipelines run under the bottom of the car and are attached to it with clamps and screws. Periodically, pipelines and their fastenings should be inspected for the presence of cracks and dents.
3. If dirt is found in the fuel filter during inspection, the pipelines must be disconnected and blown out. Check the strainer in the pump fuel pickup pipe for damage (see paragraph 5).
Steel pipelines
4. If it is necessary to replace the fuel line or exhaust pipe, use for this purpose seamless or welded pipes of the dimensions that were installed by the vehicle manufacturer.
5. Do not use copper or aluminum pipes to replace steel pipes. These materials cannot withstand normal vibrations. occurring in the vehicle.
6. Since the fuel lines on vehicles with fuel injection are always under pressure, they must be treated with particular care.
7. Some pipelines have o-ring threaded fittings. When disconnecting them, the following rules must be observed.
- A) Always hold the other half of the connection with an open end wrench to avoid twisting the piping.
- b) Inspect all joint sealing pins for cracks, cuts, and rubber degradation. Replace seal. if it is hardened, worn or its condition is questionable.
- V) When replacing pipelines or their connections, purchase brand-name parts whenever possible, or at least use a source that you can trust.
Flexible hoses
Caution: Purchase only brand name or equivalent replacement hoses. Not every hose will be able to work under the pressure created by this system.
8. Do not lay fuel hoses closer than 0.1 m from mufflers and exhaust pipes, or closer than 0.25 m from the catalytic converter. Fasten the pipelines so that they do not rub against the body parts. To do this, a gap of at least 8 mm must remain between the pipeline and the body.
Removal and installation
9. Relieve the pressure in the fuel system (see paragraph 2).
10. Release the pipeline from fastenings to a body.
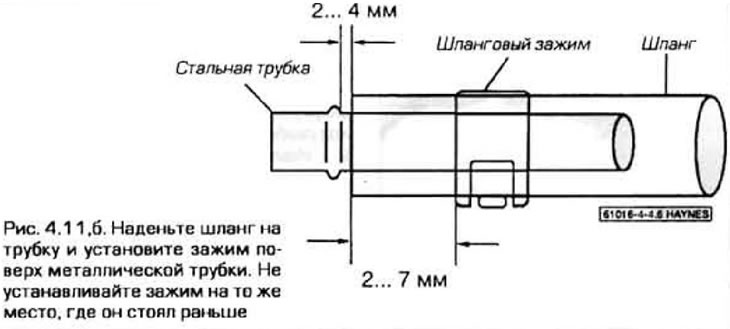
11. In most cases, flexible hoses are connected to steel pipes using spring clamps (pic. 4.11,a). To loosen such a fastener, squeeze the bent ends of the clamp with pliers and slide it along the hose. Do not reuse such a clip if it is bent or has lost its elasticity - it is better to replace it. Insert the metal tube into the hose at least 25 mm and position the clamp over the metal tube (pic. 4.11b).

12. Some pipelines are equipped with quick couplings (pic. 4.12). To disconnect such pipelines, squeeze the protrusions of the connector and pull the pipes in different directions.
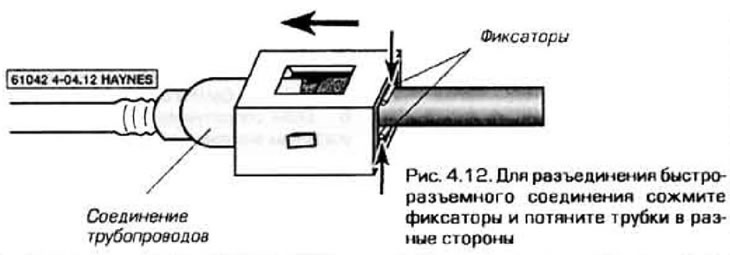
Caution: Do not unnecessarily remove the connector piece from the metal tube. After re-installing it, you are unlikely to be able to ensure the tightness of the connection.
13. Connection of pipelines is carried out in the reverse order of their separation. Push the halves of the quick coupling into each other until the latches snap into place.
Repair
14. In case of damage to the pipeline element (hose or steel tube) the defective part should be replaced with the same branded one. Parts of dubious origin may not withstand the high pressure generated by the system.
