Carburetor
Aisan emulsion type carburetor, two-chamber, with sequential opening of throttle valves, with automatic starting device.
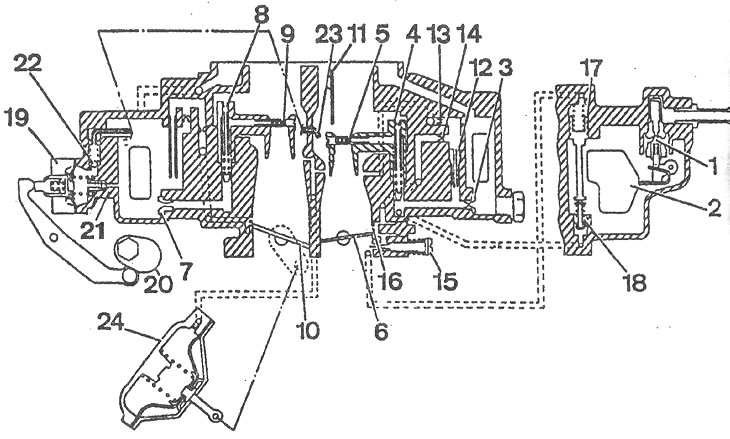
Aisan carburetor diagram: 1 - needle valve; 2 - float; 3 - main fuel jet of the 1st chamber; 4 - main air jet of the 1st chamber; 5, 9 - sprayers; 6 - throttle valve of the 1st chamber; 7 - main fuel jet of the 2nd chamber; 8 - main air jet of the 2nd chamber; 10 - throttle valve of the 2nd chamber; 11 - air damper; 12 - idle fuel jet; 13 - idle air jet; 14 - idle fuel channel; 15 - quality adjustment screw (composition) mixtures; 16 - slot of the transition system of the 1st chamber; 17 - economizer channel piston; 18 - economizer valve power modes; 19 - diaphragm accelerator pump; 20 - accelerator pump drive cam; 21, 22 - check ball valves; 23 - accelerator pump sprayer; 24 - throttle actuator of the 2nd chamber.
Automatic starter
Air damper 11 (see picture) is held in the closed position by a bimetallic spring 25 and a system of levers, the throttle valve of the 1st chamber is ajar, i.e. it has a starting clearance that corresponds to a reliable start of a cold engine.
When starting the engine, the vacuum in the cylinders creates a significant suction effect with a limited amount of air.
After the engine starts to work, the vacuum in the intake pipeline acts on the diaphragm of the pneumatic actuator 26, which slightly opens the air damper 11 in order to enrich the combustible mixture at a minimum level when the engine warms up.
As the engine warms up, the opening of the air damper is provided by a bimetallic spring, which is heated by a resistor connected directly to the battery charge circuit.
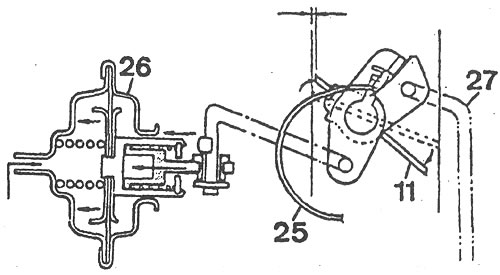
Automatic carburetor starter: 11 - air damper; 25 - bimetallic spring; 26 - pneumatic actuator of the air damper; 27 - draft for opening the air damper with an increase in the engine speed.
Idle system and transition systems
When the engine is idling, the throttle valve 6 of the 1st chamber is closed. The idle system takes fuel from the emulsion well after the main fuel jet 3 and brings it to the idle fuel jet 12. At the outlet of this jet, the fuel mixes with air passing through the air jet 13. The emulsion exits under the throttle valve through the hole of the quality adjusting screw 15 (composition) idling mixture, while the amount is determined by the amount of opening of the throttle valve 6 of the 1st chamber.
When the throttle valve is opened, the emulsion also flows through the slot of the transition system of the 1st chamber 16, which ensures a smooth transition from idling to load modes of the engine. The 2nd chamber has only a transitional system.
Main dosing system
Fuel through the needle valve 1 is fed into the float chamber, in which the float 2 pivotally mounted on the axis maintains a constant fuel level in the chamber.
From the float chamber, fuel enters through the main fuel jet 3 into the emulsion well. When the throttle valve of the 1st chamber is open, a vacuum is formed in its atomizer, under the influence of which the fuel in the emulsion well rises and mixes with air leaving the emulsion tube hole, made integral with the main air jet 4. Through the atomizer 5, the fuel-air emulsion enters diffusers and further into the mixing chamber of the carburetor.
With the throttle valve of the 2nd chamber open, the operation of the main dosing system of the 2nd chamber is similar.
The throttle valve of the 2nd chamber opens when moving under the action of a vacuum of the diaphragm of the pneumatic actuator 24, which is connected by a rod to the throttle valve 10 of the 2nd chamber. Due to the presence of a mechanical interlock, the throttle valve of the 2nd chamber opens only when the throttle valve of the 1st chamber is open and the engine is warm.
Accelerator pump
When the throttle valve of the 1st chamber is opened, the cam 20, mounted on its axis, presses the lever and acts on the diaphragm of the pump 19 through the spring in the pusher. 2 cameras.
When the throttle valve of the 1st chamber is closed, fuel from the float chamber is sucked into the cavity of the accelerator pump. Check ball valves close the inlet and outlet channels in series.
