Design and principle of operation
The power window motor is equipped with a connector and a gear.
Two proximity switches on the Hall sensor are installed in the socket.
The proximity switch on the hall sensor uses a set of magnets on a rotating shaft to sense the rotation of the power window motor and outputs a timed pulse to the main power window switch.
The proximity switch on the No. 1 Hall sensor emits one pulse each revolution of the window motor shaft. Accordingly, the power window main switch determines the angular speed of rotation of the electric motor.
The main switch determines the direction of rotation of the power window motor by the difference between the highest and lowest points of the pulse from each proximity switch on the No. 1 and 2 Hall sensors.
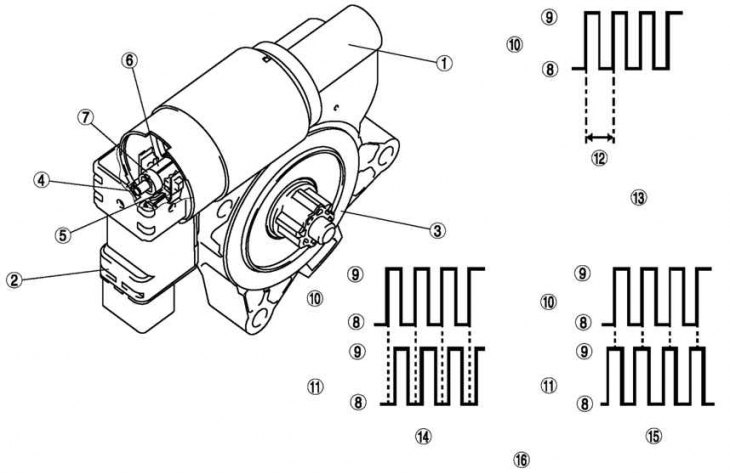
Pic. 8.31. Power window motor with servo: 1 - electric motor; 2 - connector; 3 - gear; 4 - contactless switch on the Hall sensor No. 1; 5 - contactless switch on the Hall sensor No. 2; 6 - shaft; 7 - magnet; 8 - low; 9 - high; 10 - impulse (proximity switch on hall sensor no. 1); 11 - impulse (proximity switch on hall sensor no. 2); 12 - one revolution of the power window motor with a servo drive; 13 – detection of glass movement distance; 14 - up; 15 - down; 16 - detection of the direction of glass movement
