When the xenon is energized, the temperature inside the discharge headlight bulb rises, evaporating the mercury, and an electric arc occurs.
Mercury and an electric arc cause a further increase in temperature inside the lamp, iodide evaporates and decomposes, metal atoms give off the accumulated energy, producing light.
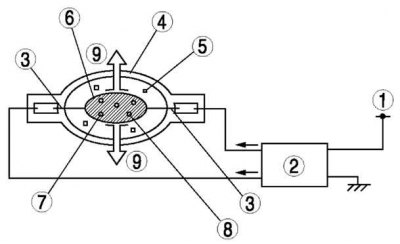
Pic. 7.13. Gas discharge headlight design: 1 - B +; 2 – the control unit of a gas-discharge headlight; 3 - conclusion; 4 – a lamp of a gas-discharge headlight; 5 – xenon gas; 6 – metal atoms; 7 - iodide; 8 - mercury; 9 - light
