The sealed type cooling system includes a belt driven water pump, radiator fan, radiator, expansion tank, heater thermostat and radiator, hoses and switches. When starting a cold engine, coolant circulates around the cylinder block and head. The warm coolant flows through the heater core to the water pump. Since the coolant expands when heated, its level in the expansion tank rises. The flow of coolant through the radiator is stopped by closing the thermostat. When the coolant reaches a certain temperature, the thermostat opens and hot coolant flows through the hose to the radiator. As the coolant passes through the radiator, it is cooled by the flow of oncoming air.
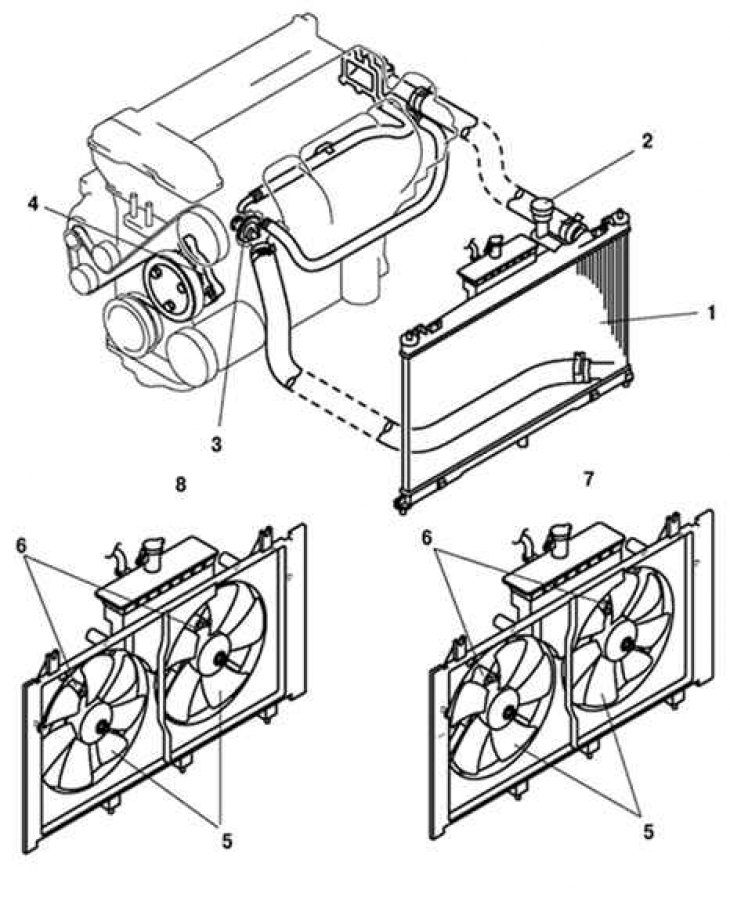
Pic. 2.47. Mazda 6 cooling system components: 1 - radiator; 2 - radiator cap; 3 - thermostat; 4 - coolant pump; 5 – fan blade of the cooling system; 6 - cooling system fan motor No. 1, cooling system fan motor No. 2; 7 - engines L3; 8 - LF engines, except for engines for L8
The thermostat housing is located near the radiator on four-cylinder engines and at the top rear of the engine on six-cylinder engines (pic. 2.47).
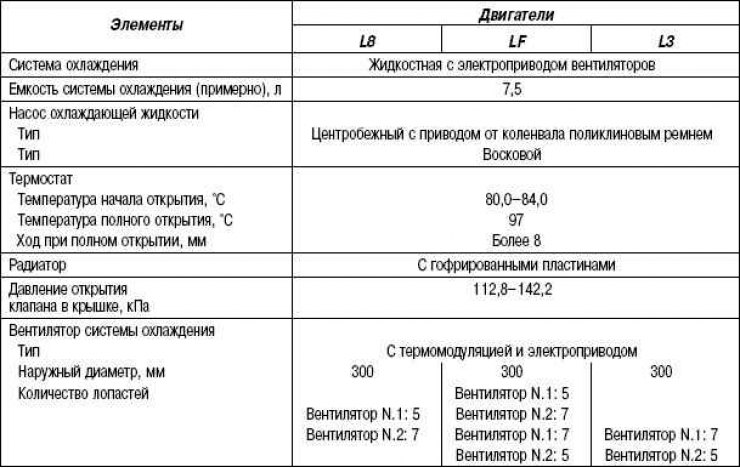
Table 2.17. Specifications of the cooling system
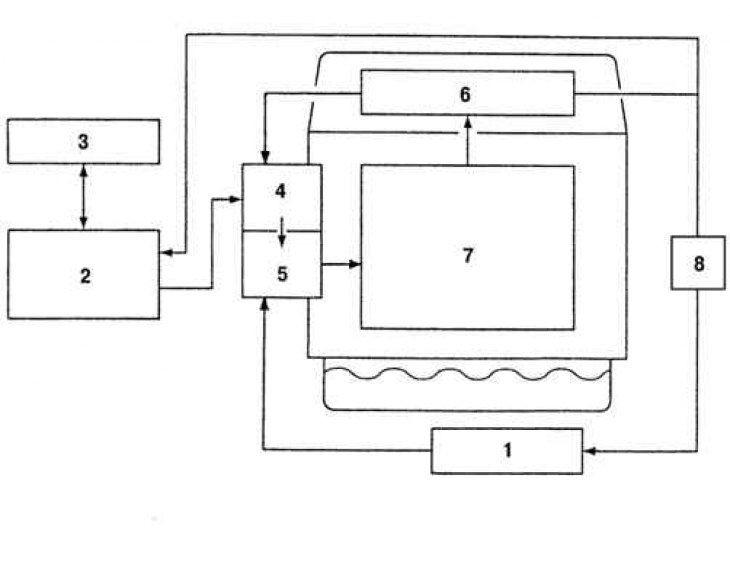
Pic. 2.48. Block diagram of the cooling system for LF and L3 engines: 1 - heater; 2 - radiator; 3 – an expansion tank of a refrigerant; 4 - thermostat; 5 - coolant pump; 6 – a head of the block of cylinders; 7 – block of cylinders; 8 - oil cooler
