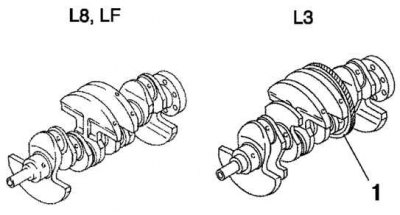
Pic. 2.8. Crankshafts for L8, LF and L3 engines: 1 - drive gear
The crankshafts of the L8 and LF models are cast iron 5-bearing with 4 counterweights. The crankshaft of the model L3 engine is cast iron 5-bearing with 8 counterweights. The balance shaft drive gear is mounted on the crankshaft. Conventional dowel key is not used, the crankshaft pulley bolt tightening torque secures the crankshaft sprocket. When installing the crankshaft sprocket, it is necessary to use a special tool for setting the TDC of the first cylinder (pic. 2.8).
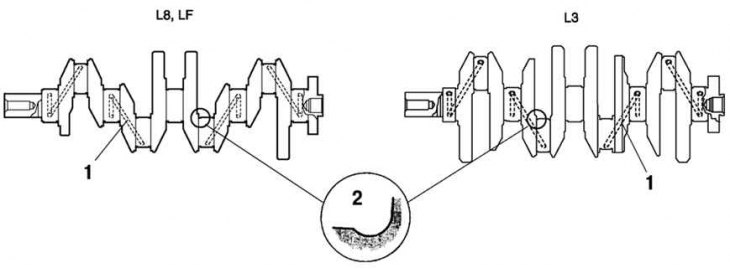
Pic. 2.9. Oil channels of the crankshaft: 1 - channel for lubrication; 2 - fillet
The oil line for supplying oil to the crankshaft main journals is located in the crankshaft. The necks and fillets of the crankshaft journals are knurled to improve load characteristics.
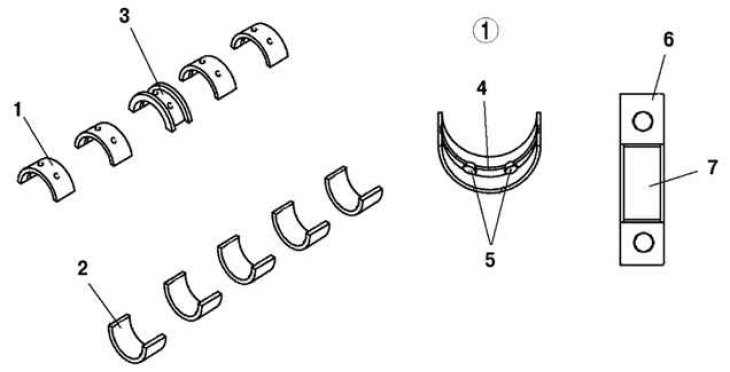
Pic. 2.10. Upper and lower shells and main bearing: 1 – a bolt of fastening of a head of the cylinder; 2 - release side; 3 - inlet side; 4 - the front of the engine; 5 – angle between two valves; 6 - inlet channel; 7 - inlet channel
The upper and lower main bearing shells are made of aluminum alloy. The top loose leaf of the bearing No. 3 - persistent. The top bearings have lubrication grooves and oil channels. There are no mounting tabs for the top and bottom bushings. Before installing the upper and lower main bearing shells, you must measure them and install them so that they are located in the center of the bearing cap (pic. 2.10).
Table 2.2. Types of liners of main bearings, mm