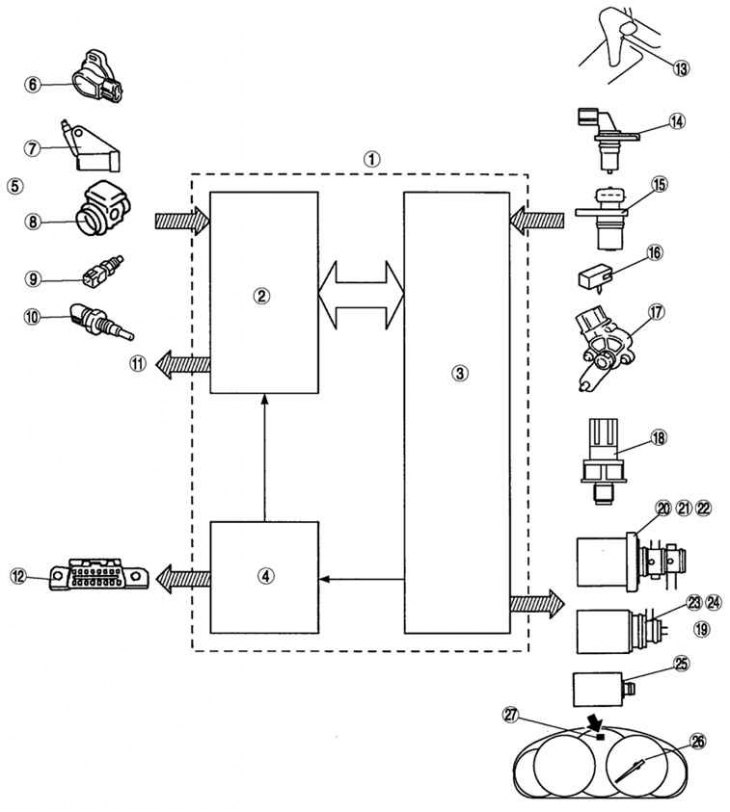
Pic. 3.75. Mazda 6 control system block diagram: 1 - PCM block; 2 - engine management system; 3 - control system of the gearbox in the block with the main gear; 4 – system of onboard diagnostics; 5 – input signals; 6 - throttle position sensor; 7 - crankshaft position sensor; 8 - mass air flow sensor; 9 – the switch of signals of braking; 10 - engine coolant temperature sensor; 11 – engine control output signals; 12 – communication channel connector; 13 – HOLD mode switch; 14 – turbine speed sensor; 15 - vehicle speed sensor; 16 - gearbox fluid temperature sensor in the block with the main gear; 17 – the switch of ranges of an automatic transmission; 18 - oil pressure sensor; 19 - output signals; 20 - switching solenoid A; 21 - switching solenoid B; 22 - switching solenoid C; 23 - switching solenoid D; 24 - switching solenoid E; 25 - pressure control solenoid; 26 - speedometer signal; 27 - control lamp of the HOLD mode
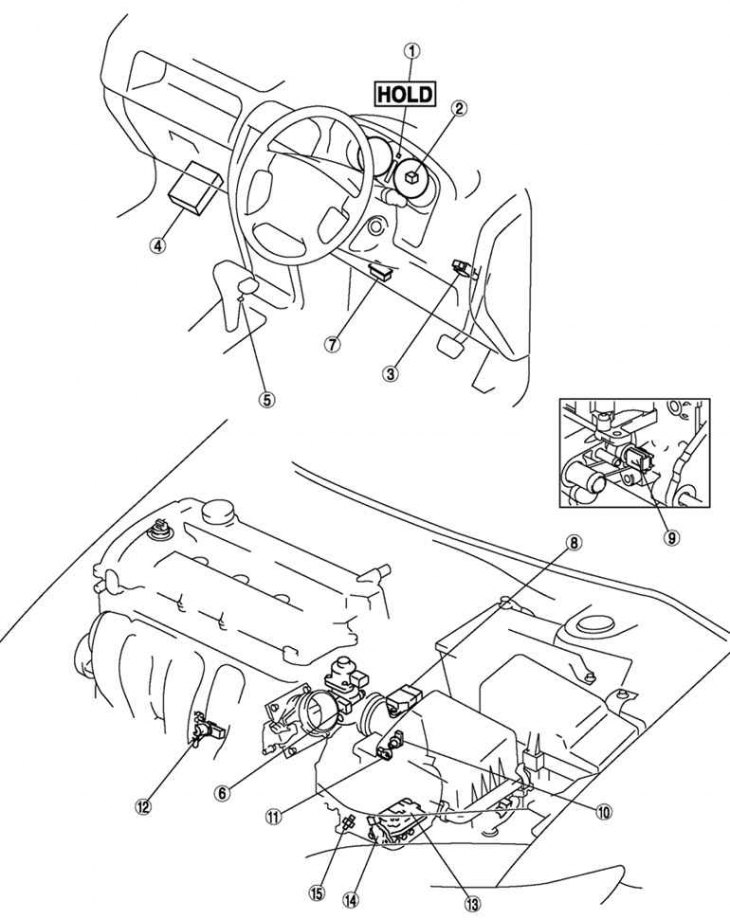
Pic. 3.74. Mazda 6 electronic control system: 1 - control lamp of the HOLD mode; 2 – speedometer; 3 – the switch of signals of braking; 4 - block PCM; 5 – HOLD switch; 6 - throttle position sensor; 7 - DLC; 8 - mass air flow sensor; 9 - engine coolant temperature sensor; 10 - vehicle speed sensor; 11 – turbine speed sensor; 12 - crankshaft position sensor; 13 - control valve (with transmission fluid temperature sensor and solenoid valves); 14 – the switch of ranges of an automatic transmission; 15 - oil pressure sensor
The automatic transmission control unit is responsible for the operation of the pump, control valve, solenoid valves, hydraulic accumulators, lockup clutches and brakes. The main pressure in the hydraulic system of an automatic transmission is created by a pump, it is regulated by the control system depending on the load and speed of the vehicle and ensures the operation of the torque converter, lock-up clutches and brakes.
Shift valves control fluid flow to the torque converter and planetary gearbox.
The valve block has three solenoid valves that control gear shifting and torque converter lockup.
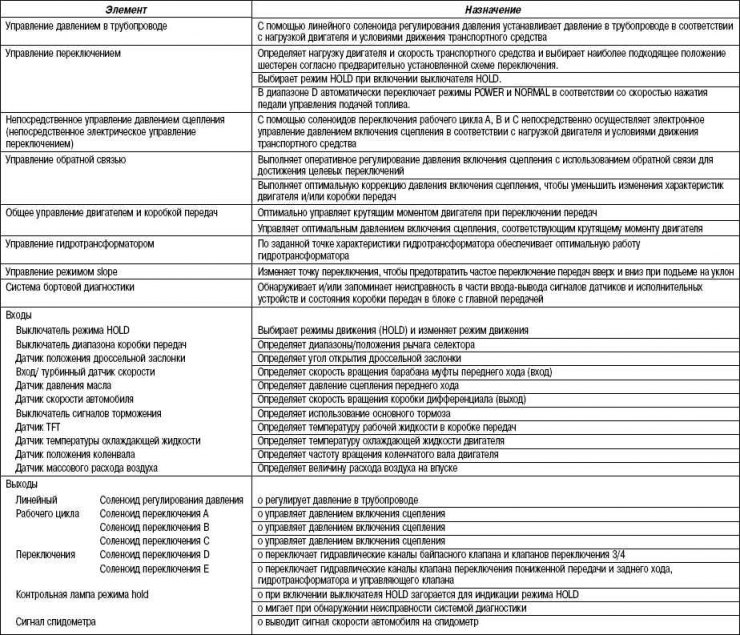
Table 3.5. Electronic controls and their operation
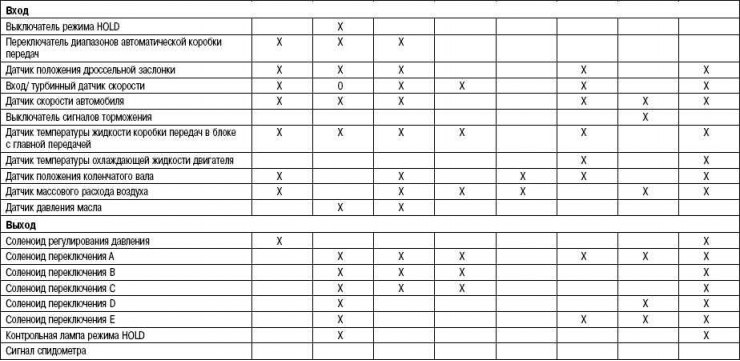
X - available;
0 - reserve;
