Accurate wheel geometry measurements cannot be made without the appropriate equipment. Therefore, the description in this chapter is limited to explaining the basic necessary concepts.
Convergence /camber /transverse tilt of the axis of rotation / longitudinal tilt of the axis of rotation
Convergence denotes the lateral distance between the wheels. Positive toe means that the wheels, measured at the height of the midpoints, are less apart at the front than at the rear. Negative convergence (discrepancy) means that the fronts of the wheels stand slightly wider than the rears.

The toe-in and lateral tilt of the steering axle prevent the transfer of road irregularities to the steering and keep friction when cornering as low as possible.
Camber is the angle at which the plane of the wheel deviates from the vertical. The front wheels thus stand obliquely, for example, with negative camber, the lower points of the wheels are wider than the upper ones.
The lateral inclination of the axis of rotation is the angle between the axis of rotation of the steering knuckle and the vertical at the point where the wheel touches the ground, looking along the vehicle.
Pitch is the angle between the steering axis of the steering knuckle and the vertical where the wheel touches the ground, looking across the vehicle. The angle of longitudinal inclination significantly affects the stability of the front wheels. Too small an angle contributes to the deviation of the wheel from the direction of movement on bad roads or in crosswinds and, in addition, leads to the fact that after a turn the steering does not return to the straight-line position well.
Preconditions for checks
The steering is adjusted correctly.
There are no unacceptable backlashes in the steering rods and suspension, the wheels and tires are in order.
Tire pressure is correct.
The car has an operating weight: the spare wheel and the jack are in the places intended for them. In addition, there should be nothing in the car.
The car before this is strongly shaken.
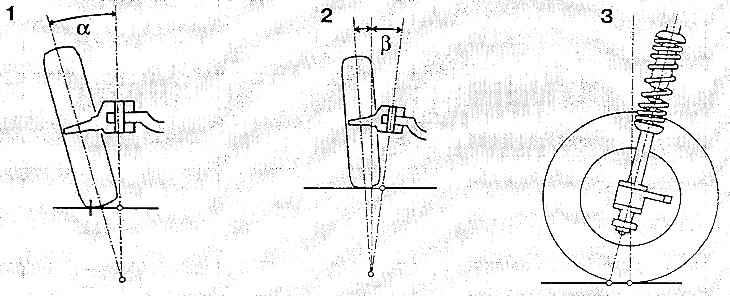
1. Collapse; 2. Lateral inclination of the axis of rotation; 3. Longitudinal inclination of the axis of rotation.
