Before concluding that the battery is faulty, check the following:
Check electrolyte density. If the density values in different banks differ from each other by no more than 0.04 g / ml, then you need to charge the battery with a normal current.
After charging, test the battery under load. If the control values are not. reached, the battery is defective.
If the electrolyte density in one or two adjacent banks is noticeably lower than in others (for example, in 5 jars 1.16 g / ml, and in one - 1.08 g / ml), then the battery has an internal short circuit and is faulty.
The battery is self-discharging
Depending on the vehicle configuration, the natural self-discharge of the battery is supplemented by current leakage in various control units at rest. Therefore, the battery in a stationary vehicle should be charged every six weeks. If leakage currents are suspected, check the electrical system as follows:
Use a charged battery for testing.
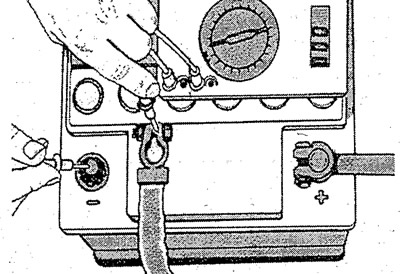
Set the maximum measurement limit on the ammeter with measurement limits of 0-5 mA and 0-5 A. Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
Attention: This will erase data from the injection system control unit, radio security codes and settings. See instructions in the relevant section of this chapter.
Connect an ammeter between the negative battery terminal and the negative cable disconnected from the battery. «Plus» ammeter connected to the wire, and «minus» ammeter - to the negative terminal of the battery.
Attention: Check can be made by means of a control lamp. If the lamp between the negative wire and the battery terminal does not light, then in any case, you must use an ammeter.
Switch off all current consumers, disconnect the clock (and other non-switchable consumers), close the doors.
Decrease the ammeter measurement limits until a readable current value is obtained.
By pulling the fuses, turn off the various circuits in turn. If, when one of the circuits is broken, the current drops to zero, then it is necessary to look for the source of the malfunction in it. Malfunctions can be as follows: corroded and dirty contacts, frayed wires, internal short circuit in the consumer itself.
If no faults are found in the fused circuits, disconnect the wires from the unfused components such as the alternator and starter.
If the current drops to zero when the wires are disconnected from unprotected units, repair or replace the corresponding unit. In case of current leakage in the starter or in the ignition system, the ignition and starter switch must also be checked.
Connect the negative cable to the battery.
Set the clock, enter the radio's security codes.
