With a very cold engine, it may be that when the air is compressed, the ignition temperature of the diesel fuel is not reached. In this case, the engine must be preheated. To do this, in each vortex chamber there is a glow plug, which heats up the combustion chamber. In addition, the diesel engine has a thermostat (with solid filling), which, through a sheathed cable, moves the injection timing regulator piston on the high pressure fuel pump in the advance direction. Due to this, fuel is injected into the hot air earlier and the cold engine starts faster. When the engine reaches its operating temperature, the thermostat element automatically returns.
Fuel is sucked from the fuel tank by the distribution injection pump. The required high pressure is created in the injection pump for diesel fuel injection (about 130 bar), and the fuel is distributed to the individual cylinders in accordance with their firing order. At the same time, the regulator in the injection pump controls the amount of injected fuel in accordance with the position of the pedal «gas». Through the nozzle, diesel fuel is injected at the right time into the prechamber of the corresponding cylinder. Due to the shape of the prechamber or swirl chamber, the sucked-in air acquires a vortex motion during the compression stroke, i.e. the injected fuel mixes with the air optimally.
Before fuel enters the injection pump, it passes through the fuel filter. Dirt and water are separated there. Therefore, it is very important that the fuel filter be replaced or water drained from it at the required frequency.
The injection pump is not serviced. All moving parts of the injection pump are lubricated with diesel fuel. The injection pump is driven from the crankshaft by a separate toothed belt.
Since diesel is a self-ignition engine, it cannot be turned off by disconnecting the voltage from the ignition system, and it has a solenoid valve installed on the injection pump. By turning off «ignition» the voltage supply to the solenoid valve is cut off, and it closes the fuel supply channel. When the engine is started, the immobilizer releases the solenoid valve and the engine starts.
Movement in winter
When the ambient temperature drops, the fluidity of diesel fuel deteriorates due to the condensation of paraffin in it. Diesel fuel becomes thick as honey. For this reason, manufacturers of diesel fuel add special additives to it in winter, which improve the fluidity of diesel fuel and guarantee engine start up to temperatures of about -20°C.
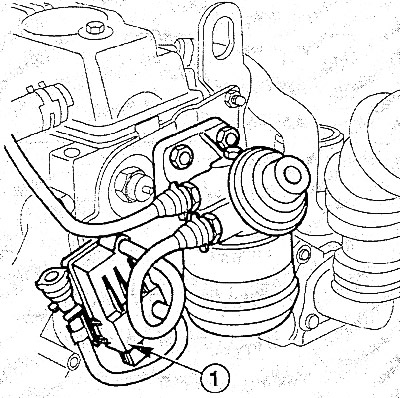
In order to prevent thickening, an electric diesel fuel heater is installed in front of the fuel filter (1). The heater is switched on by means of a built-in thermal switch independently at temperatures below 0°C. At the same time, a thermal switch protects against possible overheating of the fuel in the event of a malfunction. This ensures reliable operation at all temperatures.
Measures to improve the composition of exhaust gases
To reduce the condensation of nitrogen oxides (NOx) in the exhaust gases, an exhaust gas recirculation system is integrated into the diesel fuel injection system. The EGR valve is located in the intake manifold. Its task is to return part of the exhaust gases to the combustion chambers of the engine, while reducing the combustion temperature and therefore reducing the concentration of toxic substances in the exhaust gases.
To reduce the concentration of harmful substances in exhaust gases such as soot particles and hydrocarbons (HC or CH), requires precise electronic control and the installation of oxidation catalysts. The electronic control unit receives information from various sensors and regulates the injection process in accordance with the given databases.
One sensor determines the position of the injection pump lever controlled by the pedal «gas».
There is an inductive sensor on the flywheel of the engine. It provides information about the number of engine revolutions.
The control unit of the diesel fuel injection system selects the optimal injection moment for all engine operating modes by moving the cold start solenoid switch and the partial load solenoid valve in the injection pump.
The exhaust gas recirculation system is controlled by the control unit using two valves, a vacuum converter and an exhaust gas recirculation valve.
When the engine is cold, the control unit switches on the glow plugs and the glow plug indicator.
